Noise At Work
Hearing / Workplace HealthIf you are in a noisy job, your employer is obliged to take steps to protect your hearing, including making sure that you have hearing protection.
Protect yourself from noise exposure at work
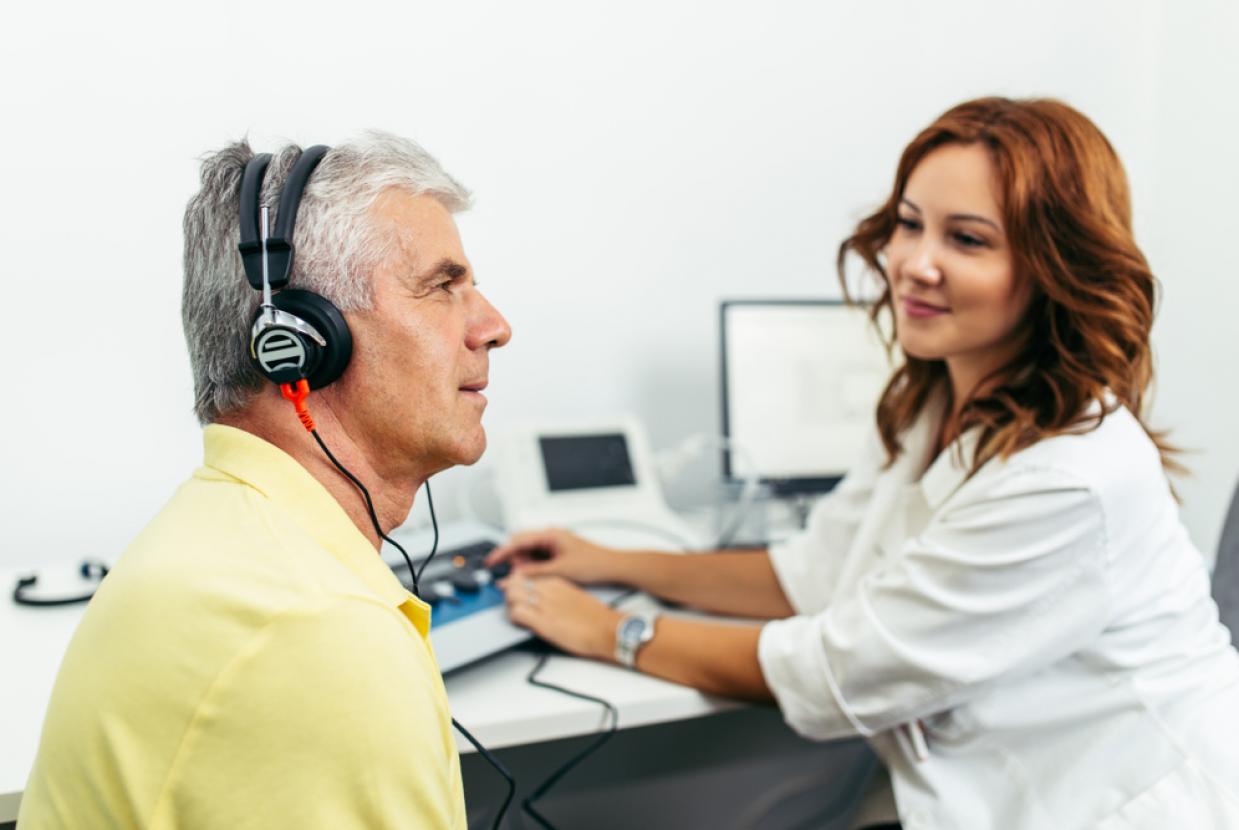
Employers have a legal duty to protect your hearing under the Control of Noise at Work Regulations (2005), which protect you if you are in a noisy job. See the HSE website for details.
The regulations say that if you are exposed to loud noise at work, your employer must have noise levels assessed, and keep a record of the assessment. You’ll know that an assessment is needed if you have to shout to communicate with someone who is two metres away from you.
If noise exposure reaches 80 decibels (dB), employers are legally bound to start taking action.
If you work in a noisy environment – such as construction, manufacturing or in a music venue or if your work involves listening to loud sounds through headphones or earpieces – your employer should make sure that you have hearing protection. For more about noise at work in the music and entertainment industry, see the Sound Advice website.
Compensation for noise damage to hearing
If you feel that your current or previous employer has failed to protect you in the workplace, and this was the cause – or part of the cause – of damage to your hearing, then you can try to get compensation. To get this, you will need to bring a successful claim for personal injury through the civil courts. You are strongly advised to get legal advice.
Industrial Injuries Disablement Benefit (IIDB) compensates people who have become disabled as a result of an industrial disease or an accident at work. You can claim for it even if you’re still working. But it is restricted to certain occupations that are known to be noisy.
The armed forces
If you have hearing loss due to service in the armed forces on or after 2005, you may be able to claim under the Armed Forces Compensation Scheme. This scheme replaces the War Disablement Pension for people who have become disabled (including hearing loss) while serving in the armed forces before April 2005.