Overactive Thyroid
An overactive thyroid, also known as hyperthyroidism or thyrotoxicosis, is where the thyroid gland produces too much of the thyroid hormones. The thyroid is a small butterfly-shaped gland in the neck, just in front of the windpipe (trachea). It produces hormones that affect things such as your heart rate and body temperature.
Having too much of these hormones can cause unpleasant and potentially serious problems that may need treatment. An overactive thyroid can affect anyone, but it's about 10 times more common in women than men, and typically happens between 20 and 40 years of age.
Symptoms of an overactive thyroid
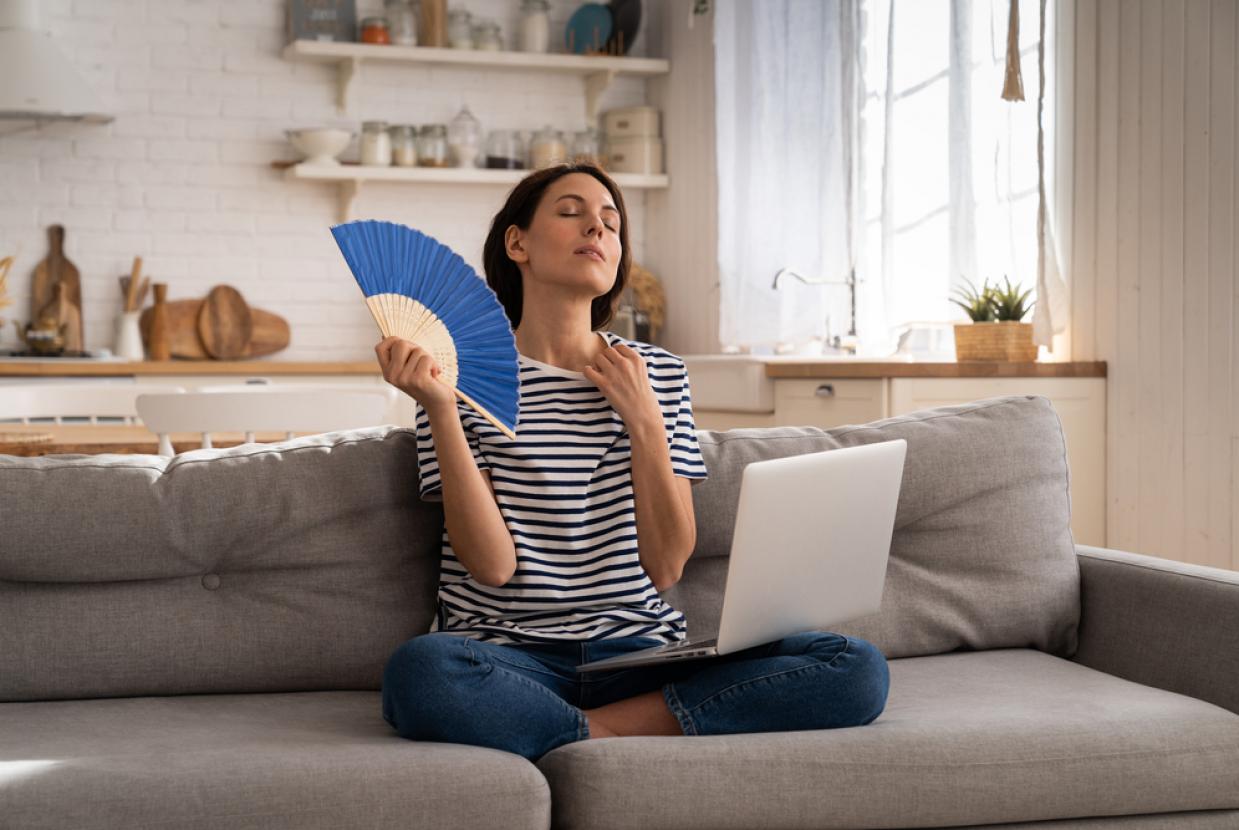
An overactive thyroid can cause a wide range of symptoms, including:
- nervousness, anxiety and irritability
- mood swings
- difficulty sleeping
- persistent tiredness and weakness
- sensitivity to heat
- swelling in your neck from an enlarged thyroid gland (goitre)
- an irregular and/or unusually fast heart rate (palpitations)
- twitching or trembling
- weight loss
When to see a GP
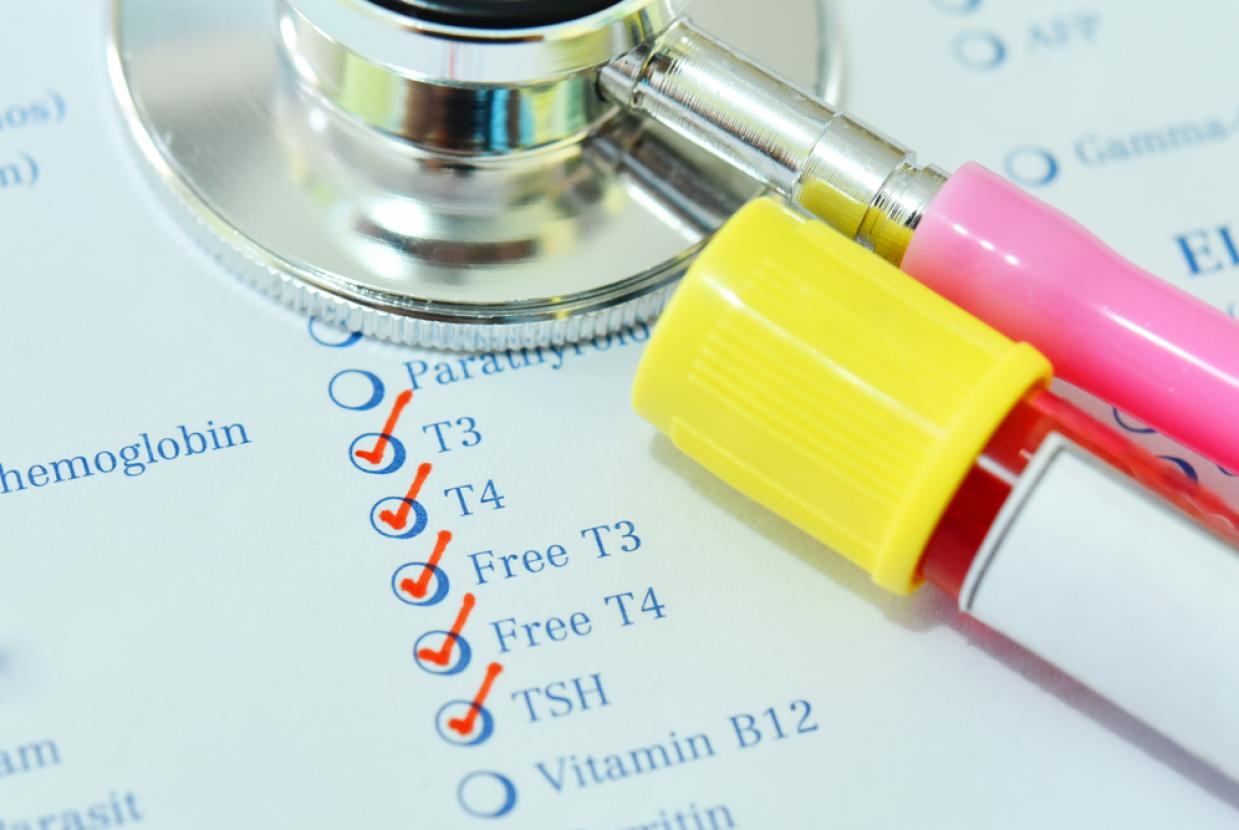
See a GP if you have symptoms of an overactive thyroid. They'll ask about your symptoms and if they think you might have a thyroid problem, they can arrange for a blood test to check how well your thyroid is working. If the blood test shows that you have an overactive thyroid, you may be referred for further tests to identify the cause.
Treatments for an overactive thyroid
An overactive thyroid is usually treatable. The main treatments are:
- medicine that stops your thyroid producing too much of the thyroid hormones
- radioiodine treatment – where a type of radiotherapy is used to destroy cells in the thyroid, reducing its ability to produce thyroid hormones
- surgery to remove some or all of your thyroid, so that it no longer produces thyroid hormones
Each of these treatments has benefits and drawbacks. You'll usually see a specialist in hormonal conditions (endocrinologist) to discuss which treatment is best for you.
Causes of an overactive thyroid
There are several reasons why your thyroid can become overactive. These include:
- Graves' disease – a condition where your immune system mistakenly attacks and damages the thyroid (about 3 in every 4 people with an overactive thyroid have Graves' disease)
- lumps (nodules) on the thyroid – this extra thyroid tissue can produce thyroid hormones, causing your levels to be too high
- some medicines such as amiodarone, which can be used to treat an irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia)