Diagnosis & Treatment
A heart attack is usually confirmed with heart tests such as an electrocardiogram (ECG) and blood tests. The ECG may be done by the ambulance crew. Treatments to try to restore blood flow to the heart are started as soon as possible.
Initial treatment will include pain relief, oxygen and a combination of medications to thin the blood, widen the blood vessels or slow down the heartbeat.
During a hospital stay, ECGs and blood tests are carried out. Other tests may also be conducted to assess how well the heart is pumping, whether blood flow has been restored and to help decide on the best form of treatment. Click here to find out more information on the types of tests which may be carried out.
Treatment
Medications – After a heart attack, you may need to take a variety of medicines. The aim of administering medication during a heart attack, and just after, is to restore blood flow, save heart tissue and prevent complications. The purpose of subsequent medication is to promote healing of your heart and prevent another heart attack.
Primary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PPCI) – This procedure improves blood flow to the heart by using a special balloon to open a blocked artery from the inside. Often a special expandable metal tube (stent) is inserted and left in place to keep the artery open.
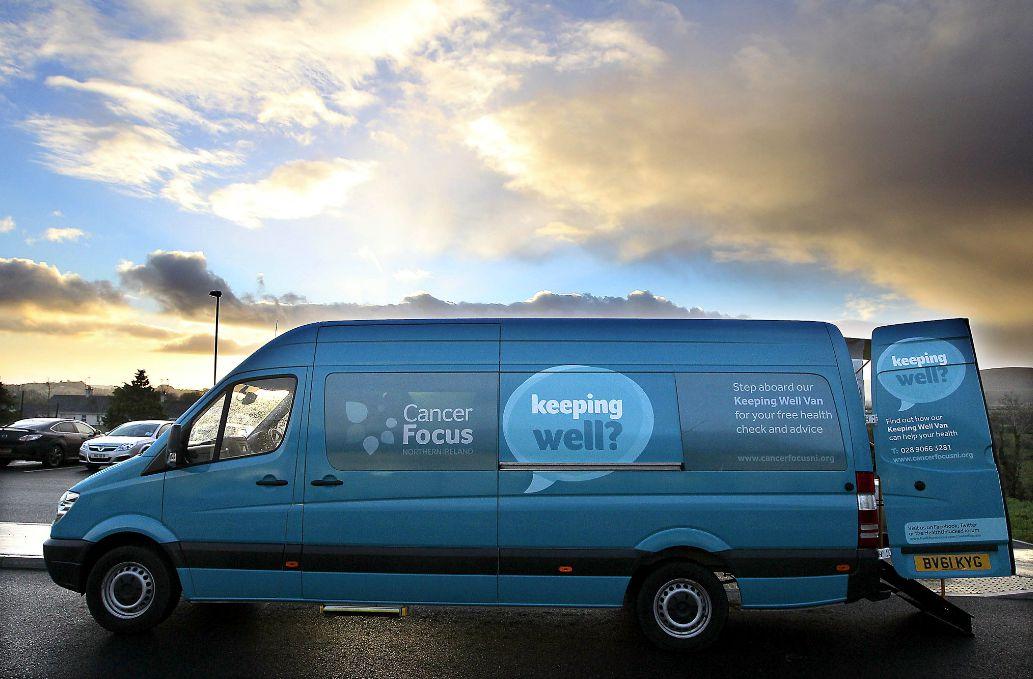
PPCI treatment is now available 24/7 across Northern Ireland. When the ambulance crew arrives, they will carry out an ECG on the patient which they forward to the specialist nurse teams at the RVH or Altnagelvin, which are Northern Ireland’s Heart Attack Centres (HACs). This highly specialist triage team then decide if the type of heart attack the patient is experiencing needs PPCI at one of the HACs or if they can be taken to their local A&E. If they are suitable for PPCI, the ambulance crew will take the patient directly to the Cath Lab for treatment, bypassing A&E. Their chance of survival are increased and their chances of reoccurrence are reduced. This is why it is important to call 999 immediately – the sooner this process starts, the better chance the patient has of a good recovery.
Coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) – Increasingly, blockages are being opened up with PCI but there are still cases where surgery is needed. In CABG, healthy arteries or veins taken from other areas in the body are used to bypass narrowed coronary arteries.