Domestic
Domestic abuse, or domestic violence, is any incident of controlling, coercive or threatening behaviour, violence or abuse between those aged 16 or over who are or have been intimate partners or family members, regardless of their gender or sexuality.
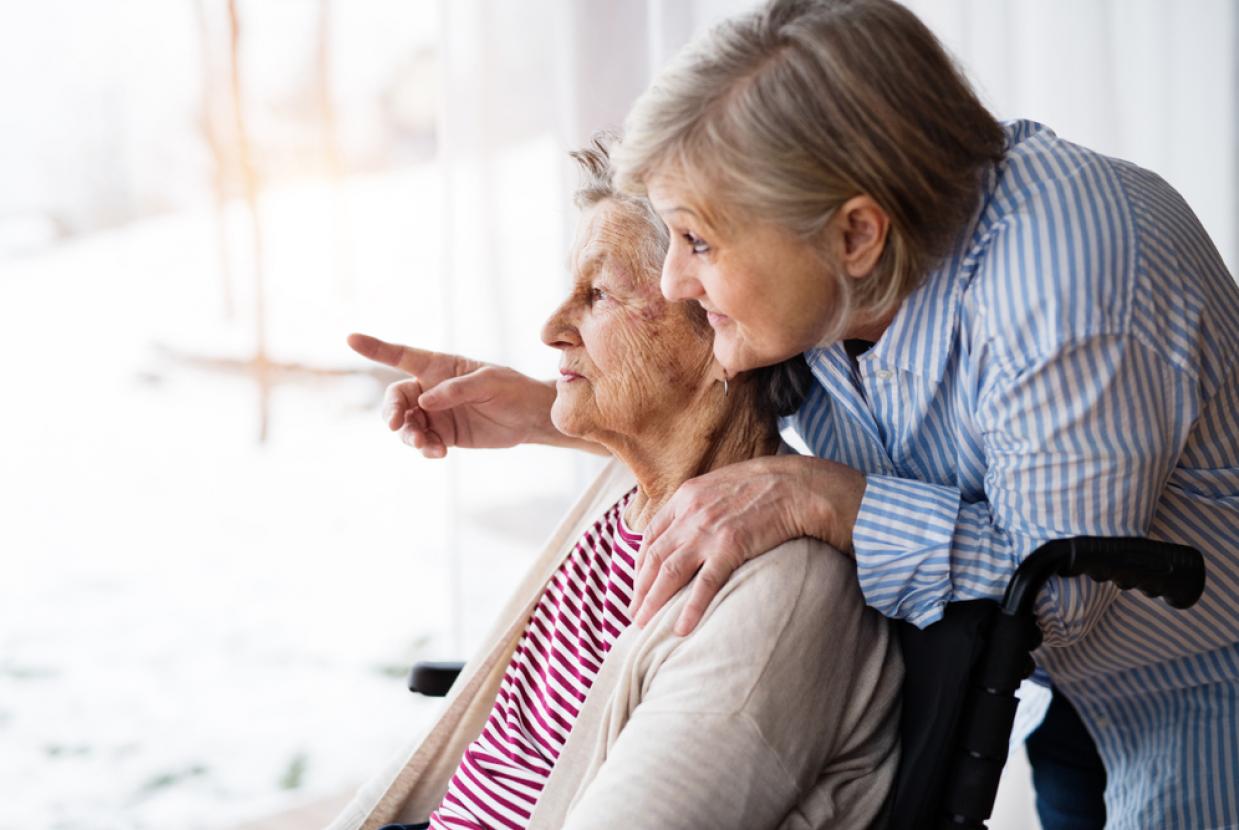
Domestic abuse and the abuse of older people are coinciding concepts. An incident of domestic violence may constitute the abuse of an older person and vice versa. Therefore the signs of abuse can be seen in acts of financial, psychological, sexual and physical abuse as well as neglect. Older people are at risk of all forms of domestic abuse.
Domestic abuse affects people of all ages. However, older victims’ experiences often differ to those of younger people, due to a variety of social, cultural and physical factors that require attention.
- For older victims, family members rather than intimate partners are most often the perpetrators of domestic abuse.
- Older women often feel expected to protect the family unit by staying with the abuser, and may fear losing relationships with adult children, family, and friends.
- For many older victims, abuse may become normalised and accepted, which can create barriers to getting help and support.
- Older victims may experience a decline in physical and cognitive health and become dependent on their abuser for support.
- In some cases older victims may also provide a caring role for their abuser which also impacts on their willingness to leave an abusive relationship.
- Ageist media and political campaigns against domestic abuse that predominantly focus on young women and children and erase the voices of older victims can contribute to barriers for older people reporting abuse and seeking help.
To view the domestic abuse information brochure, click here.