Arrhythmias
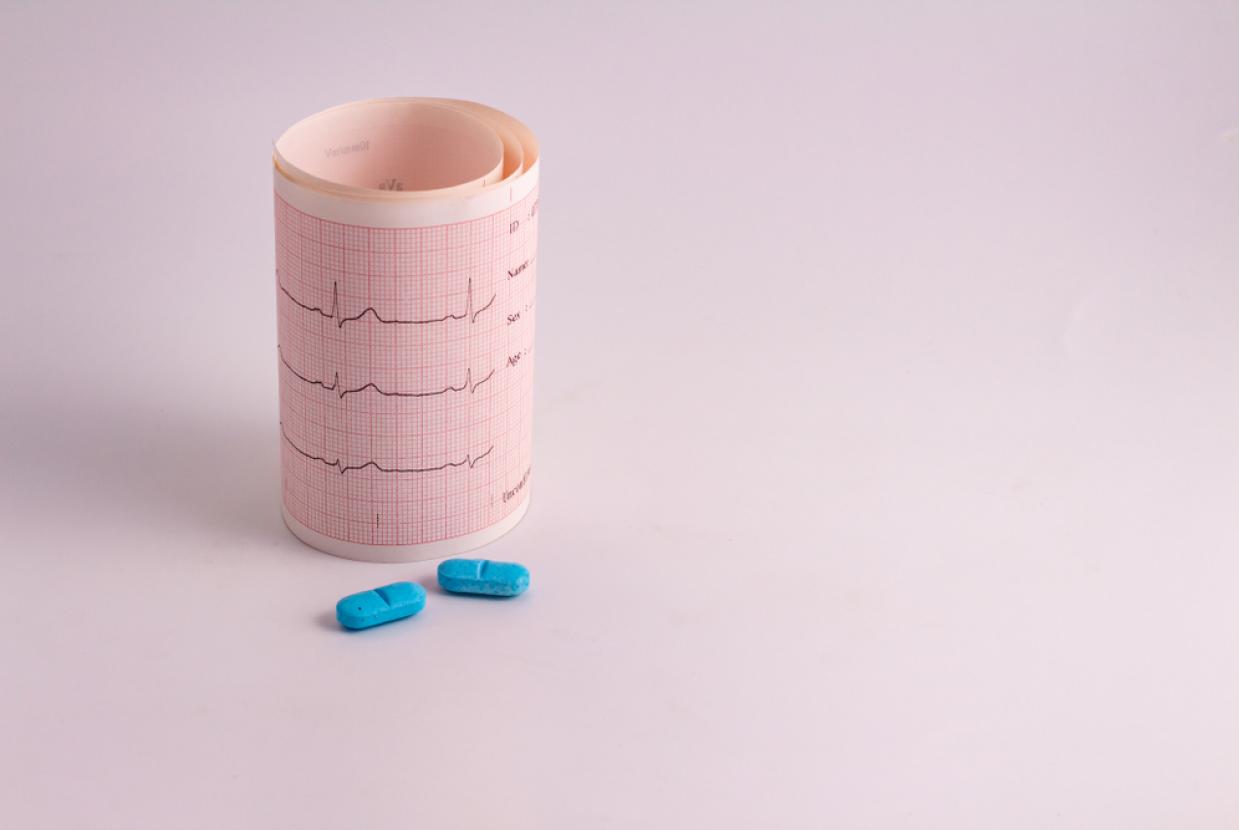
The medical term for an abnormal rhythm of the heart is arrhythmia. If the heartbeat is too slow, it is called a bradyarrhythmia or bradycardia. If it is too fast, it is called a tachyarrhythmia or tachycardia. We consider that the normal heart rate is between 60 and 100 beats per minute but there are many exceptions.
Athletic people may have heart rates less than 60 and all of us can have rates over 100 when we are exercising or under pressure etc.
Some forms of rapid heart beating can be life-threatening. When rapid heart beating arises in the ventricles – called ventricular tachycardia – a life-threatening situation can arise.
The most serious cardiac rhythm disturbance is called ventricular fibrillation when the electrical activity is so fast and chaotic that the heart cannot pump any blood.
Collapse and sudden death follows unless cardiac pulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and further medical help is provided immediately. Other non-life-threatening forms and symptoms which may require drug treatment.
Other forms of rapid heart beating are not life-threatening in the same way as ventricular tachycardia. These are called supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) during which the heart rate can increase quite suddenly to over 200 beats per minute.
This usually causes distressing palpitations often with light-headedness, chest tightness, breathlessness and other symptoms. Sometimes these episodes are short-lived and terminate spontaneously.
Other times they persist and may require drug treatment or electrical conversion in hospital. Previously, supraventricular tachycardia required long term drug therapy but more recently curative treatment with ablation has been developed.
Atrial Fibrillation (AF)
Is another form of supraventricular arrhythmia (SVT) during which the normal regular rhythmic activity of the upper chambers or atria is replaced by chaotic irregular activity.
Ectopic beats
Are early (premature) or extra heartbeats and can feel like your heart skips or misses beats. Ectopic beats happen when electrical activity arises from other cells in your heart other than the normal electrical cells (sinus node).
Most people have ectopic beats at some time in their lives, and most are unaware of having them. To learn more about heartbeats and how your heart works, see the section How Your Heart Works.