Diagnosing Breast Cancer
You usually start by seeing your GP. They will examine you and refer you to a breast clinic to see a specialist.
Or you may be referred through NHS breast screening programmes. This is usually if there are changes on your mammogram. Breast screening is a way of finding breast cancer at an early stage, when it is too small to be felt or seen.
At the breast clinic
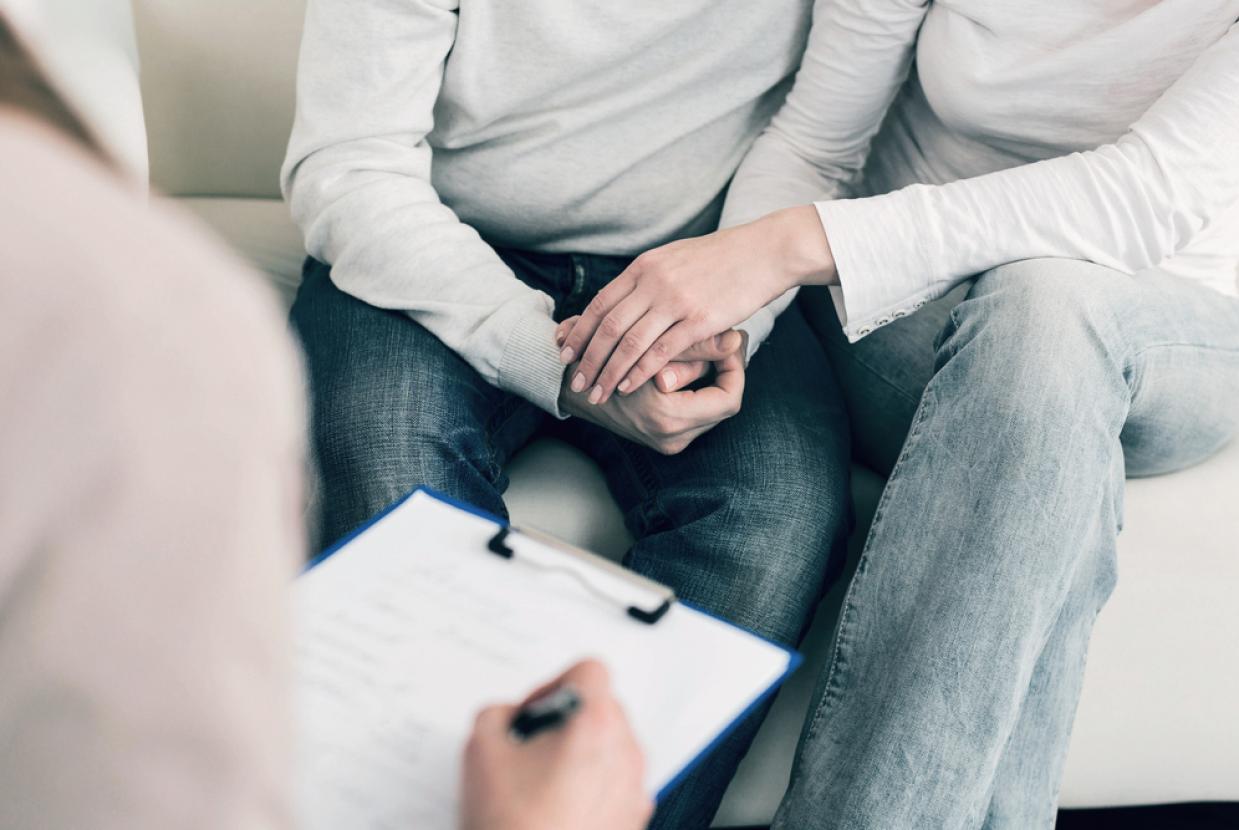
At the clinic, you will see a specialist breast doctor or a nurse. You may also see a breast care nurse. They usually ask you if:
- you have had any other breast problems or health problems
- anyone in your family has had breast cancer or ovarian cancer
- you have been through the menopause
- you are taking any medicines – for example, hormone replacement therapy (HRT) or the contraceptive pill.
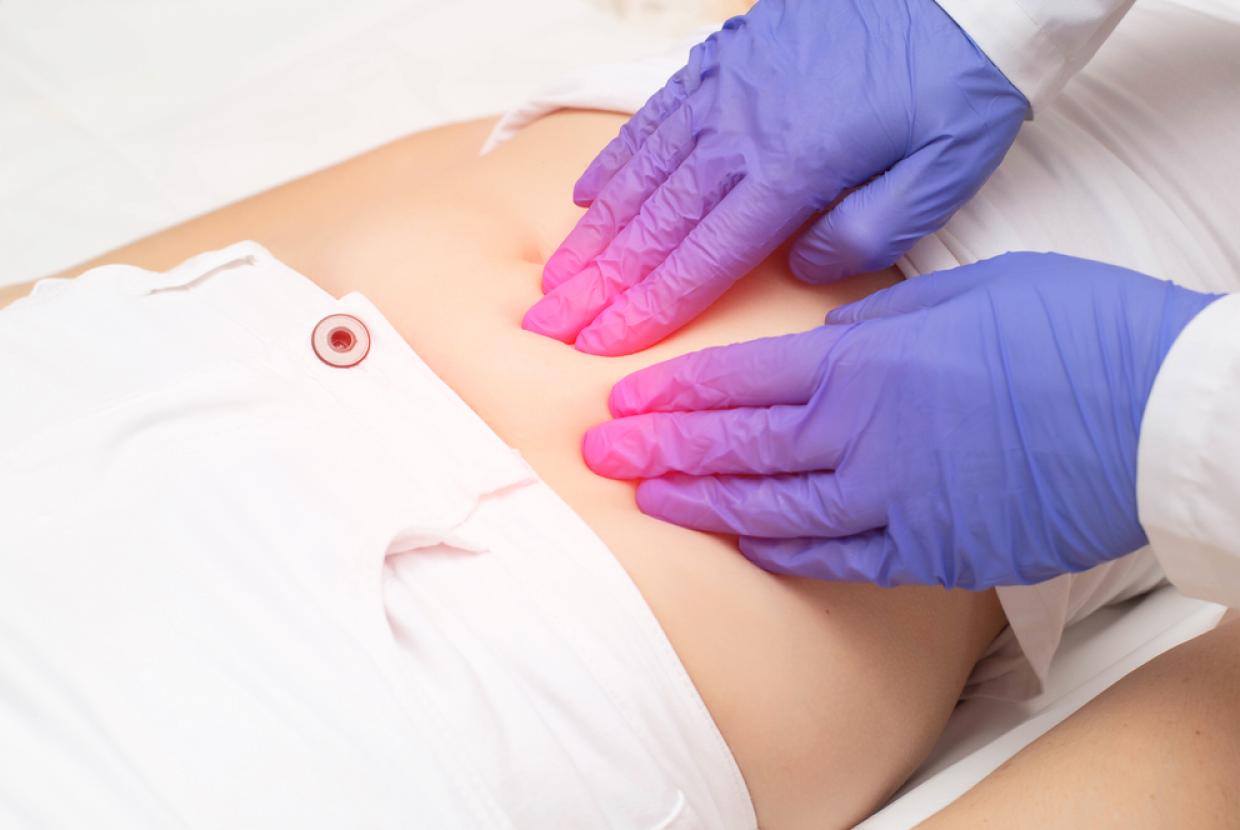
The doctor or nurse will examine your breasts and the lymph nodes in your armpits and around your neck.
Tests
After your examination, your doctor or nurse will tell you what tests you need:
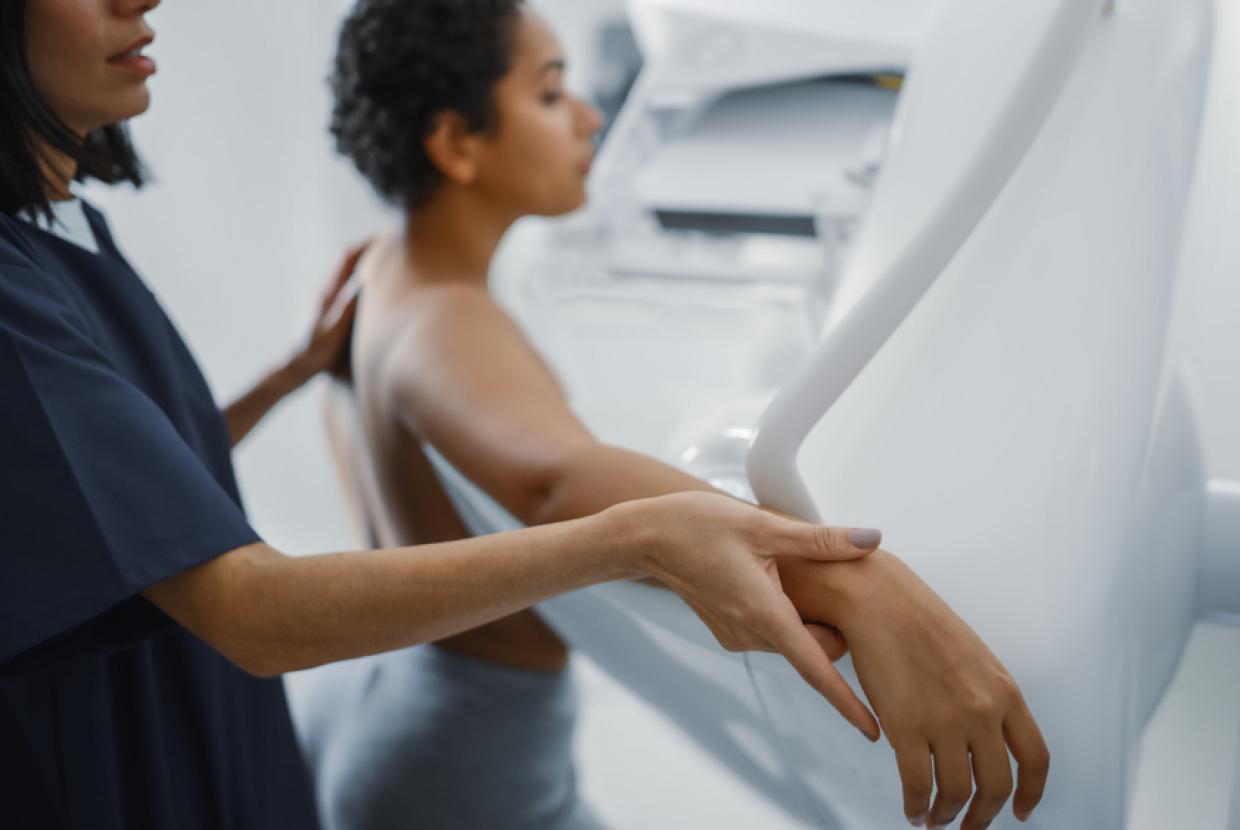
- Mammogram - A mammogram is a low-dose x-ray of the breast.
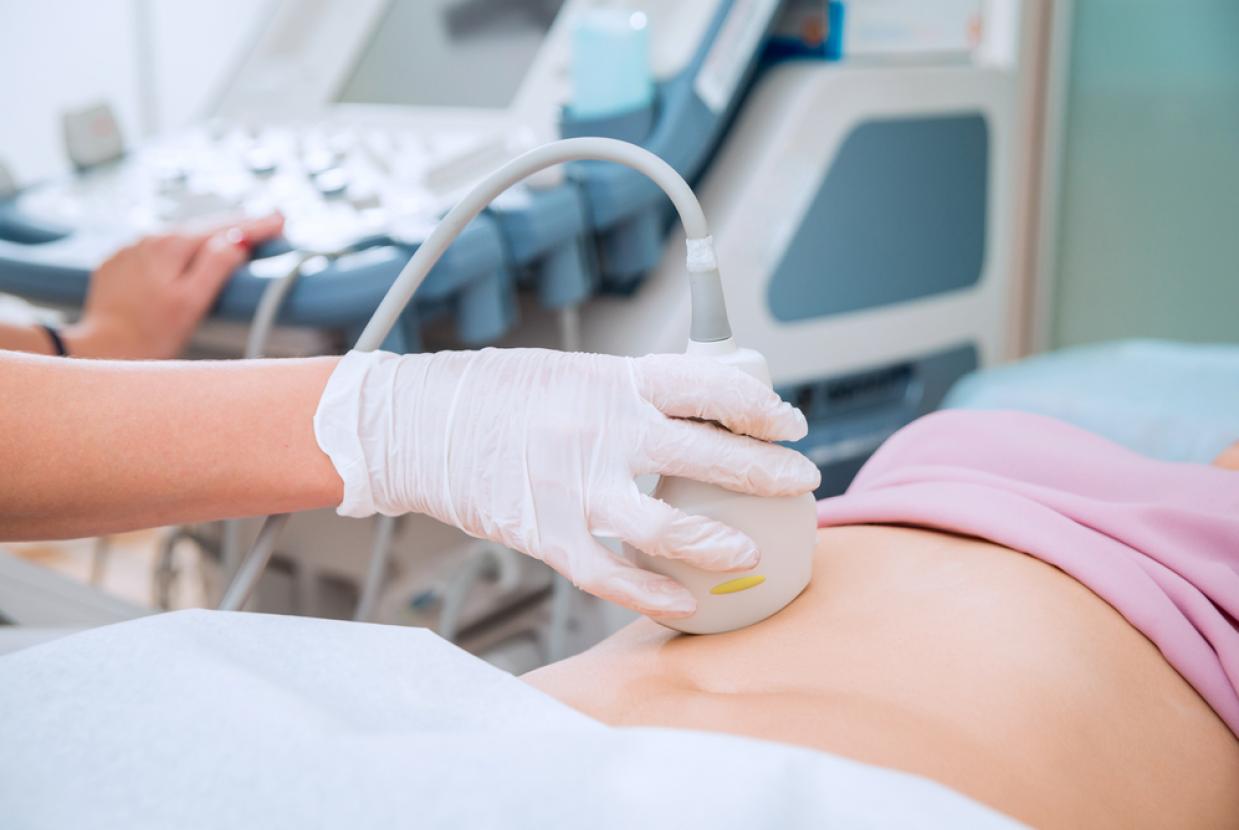
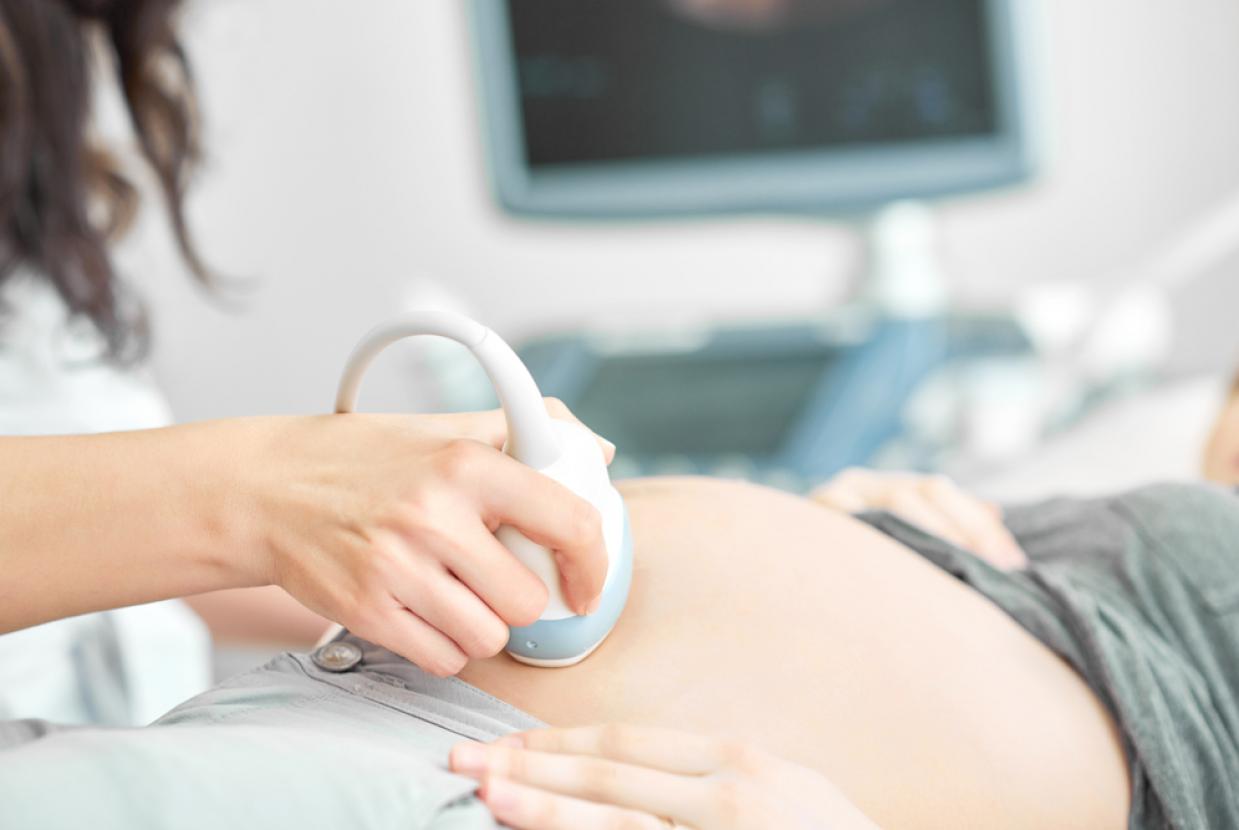
- Breast ultrasound - A breast ultrasound uses sound-waves to build up a picture of the breast tissue. You will also have an ultrasound scan of the lymph nodes in the armpit.
- Breast biopsy - During a breast biopsy, the doctor removes a small piece of tissue or cells from the lump or abnormal area. The sample is checked for cancer cells. There are different ways of taking a breast biopsy.
Further tests after diagnosis
If the biopsy results show there are breast cancer cells, you will need further tests. You may have the following tests to check your general health:
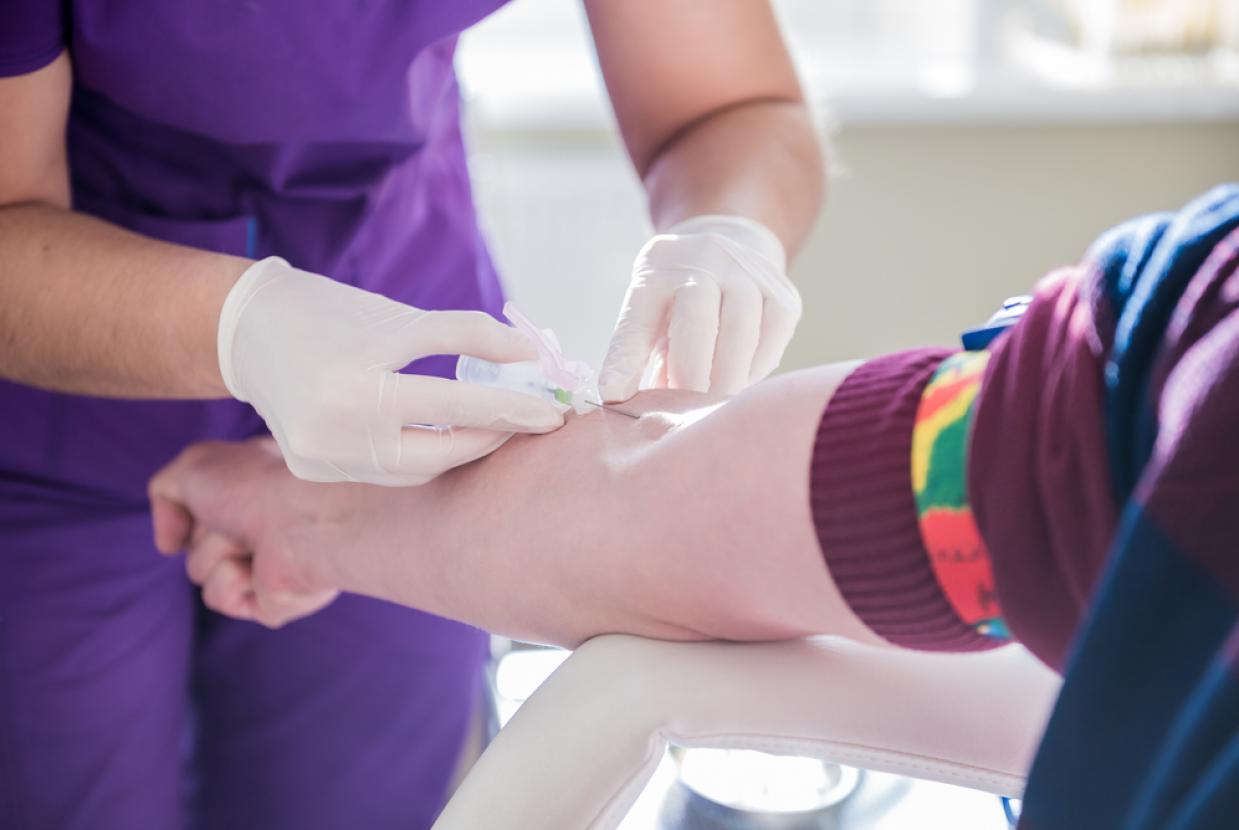
- Blood test - you have a blood test to check your general health and how well your kidneys and liver are working
- Chest x-ray - you may have tests to find out more about the size of the cancer, or if it has spread anywhere else in the body (its stage)
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) scan - an MRI scan uses magnetism to build up detailed pictures of your body. It may be done to find out the size of the cancer and help decide on the operation you have.
- CT scan - A CT scan takes a series of x-rays, which build up a three-dimensional picture of the inside of the body.
- Bone scan - A bone scan shows up abnormal areas of bone. You have a small amount of a radioactive substance injected into a vein and wait for 2 to 3 hours to have the scan.