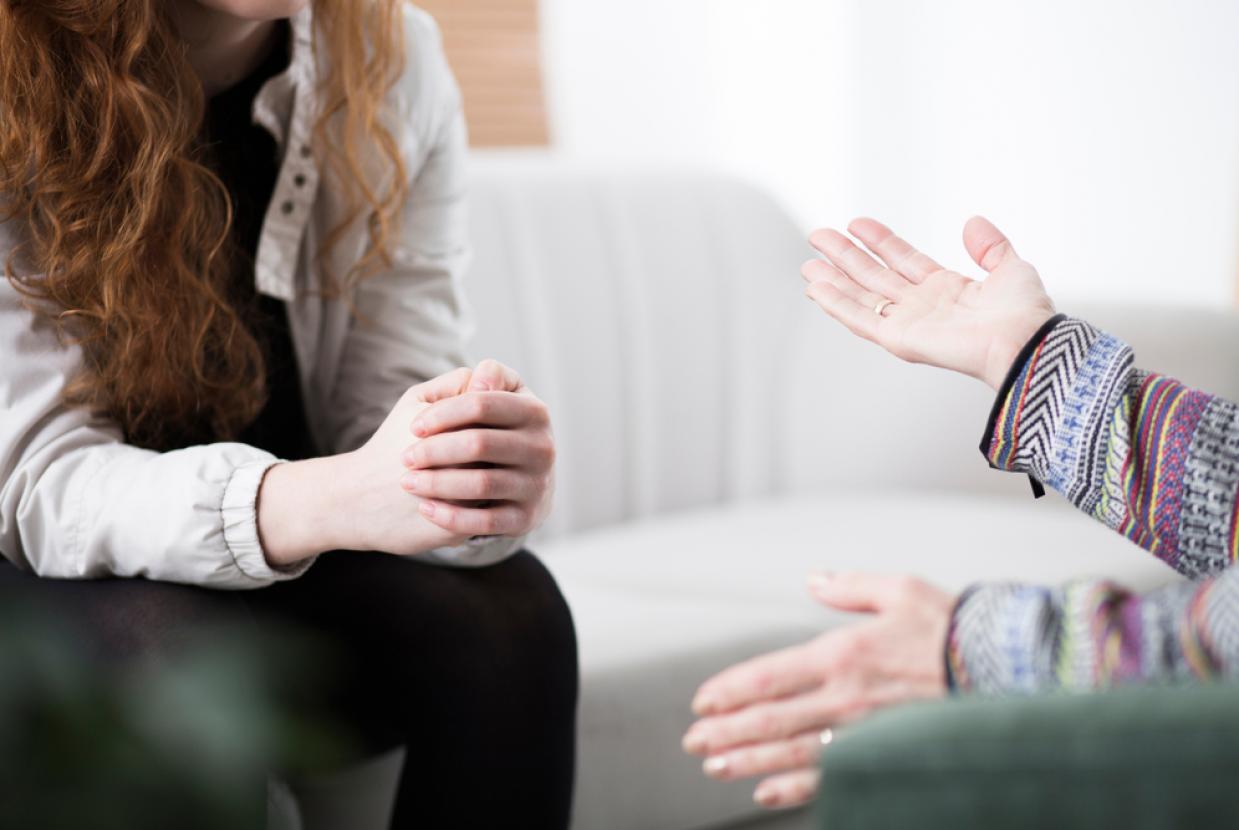
Intimacy & Cancer
Cancer and cancer treatment can affect many areas of sexual well-being. They may cause changes that are:
- physical – you may have side effects or symptoms that change how your body works or looks
- emotional – you may be dealing with stress, worry or other difficult feelings
- practical – your usual routines or roles may change.
These areas are often linked. If there is a change in one area, it may affect another. Many changes caused by cancer treatment are temporary and usually get better after treatment. As you recover, you may find your sex life goes back to the way it was. Sometimes people might have to adjust to changes that last longer or that may be permanent.
There can be ways to improve your sexual well-being and to manage any problems. But sometimes this gets forgotten because there are other things to cope with when you have cancer. It may also be ignored because you or your healthcare team feel embarrassed or worried when talking about sex.
Some people worry about whether it is safe to have sex after being diagnosed with cancer. It is important to remember that sexual touching, penetration or close physical contact:
- cannot pass cancer on to a partner
- will not affect the cancer
- does not make cancer more likely to come back.
If you feel like having sex, it is usually safe to do so. Some people find they still enjoy sex and want to keep their sex life as normal as possible.
But you should not put pressure on yourself to have sex or be intimate. Cancer and treatment can affect your sex drive in different ways. You may not feel interested or ready to have sex for a time before, during or after treatment.
Side effects and sex
Some cancer treatments may change how your body and sex organs work during sex. These may happen if a treatment affects your levels of sex hormones. Or they can happen if a treatment damages tissue, nerves or blood vessels in the pelvic area. This may include:
- surgery or radiotherapy to the pelvic area – the area below your tummy (abdomen) and between your hips
- hormone therapy – this is often used to treat breast or prostate cancer
- chemotherapy – if this causes an early menopause
- surgery or radiotherapy to the pituitary gland or brain.
Side effects of treatment that may affect sex include:
- erection or ejaculation problems and cancer
- vaginal dryness or other vaginal changes
- loss of sex drive
- changes in sexual sensation
- anal or rectal changes.
Your cancer doctor, nurse or radiographer will explain what to expect. They will also tell you whether you need to make changes to your sex life because of a treatment. Examples of these changes include the following:
- if may have had surgery or radiotherapy to the pelvic area, your body may need time to heal properly before having vaginal or anal sex.
- If you now have difficulty keeping an erection, you may need to take medication or use equipment to help.
- If you had certain types of internal radiotherapy such as seed brachytherapy or radioisotope therapy, you may be told to avoid close physical contact for a short time. This is to protect partners from radiation.
- If you had high-dose chemotherapy or a stem cell transplant, you will be advised not to have close physical contact with anyone for a while. This is to protect you from infection. Your cancer doctor or specialist nurse will explain more about this.
Treatment to other parts of the body, for example for breast cancer or head and neck cancer can also affect sex. Or you may be coping with side effects such as problems controlling your bladder or bowel (incontinence) which can also affect how you feel about sex.
Treatments can also cause general side effects that can change how you feel about your body or having sex. For example, treatment might cause tiredness (fatigue), pain or make you feel sick. This may mean you are less interested in sex. If your body or appearance changes in some way, this can also affect how you feel about your body and sex.
There are different ways of managing these changes and improving your sexual well-being. We have more information about:
- Vaginal changes, sexual well-being and cancer
- Erection problems, sexual well-being and cancer
- Side effects that affect other areas of the body.
You may also find our information about the body and sex helpful.
Having sex during treatment
If you have sex during cancer treatment, it is important to prevent a pregnancy and to protect yourself and any partners.
Preventing pregnancy
Some cancer treatments can be harmful to an unborn baby – for example, chemotherapy and radiotherapy. During your treatment and for a time after, it is important to use contraception if you or a partner could become pregnant.
Even if your cancer treatment is likely to damage your fertility, you may still be able to start a pregnancy. Your cancer doctor, specialist nurse or radiographer can tell you more about this.
If you are of childbearing age, you may be asked to take a pregnancy test before starting some types of treatment.
There are many different types of contraception. Ask your cancer doctor, specialist nurse or radiographer which type is best for you. This depends on you and the type of cancer treatment you are having. Condoms or caps (diaphragms) can be used for any type of cancer treatment.
Some hormonal contraceptives may not work during cancer treatment – for example, the pill, patch, injection or implants. This can be because of:
- the drugs you are taking
- side effects, such as diarrhoea and vomiting.
Your doctor, nurse or radiographer can tell you more about what types of contraception are safe for you to use.
Protecting partners
Small amounts of chemotherapy or other drugs can get into your body fluids. This includes fluid made in the vagina and the fluid that contains sperm. To protect any partners, your cancer doctor may advise that during treatment and for a few days after certain drugs, you use a condom:
- for vaginal or anal sex
- or a latex barrier, such as a dental dam, for oral sex.
Your cancer doctor or specialist nurse can give you more information about your treatment. If you use a lubricant, only use a silicone-based or water-based product with condoms or dental dams.
If you are having external beam radiotherapy, there is no risk to your partner during sex. But you should use contraception to prevent getting pregnant or making someone pregnant. If you are having brachytherapy to the pelvis, your radiographer will give you more information about sex during treatment.
Protecting yourself
Your cancer doctor, nurse or radiographer may also advise using condoms during chemotherapy and radiotherapy to help reduce irritation.
During treatment, you should do the following:
- Avoid giving oral sex if you have cuts or sores in your mouth. There is a risk these could become infected.
- Tell your doctor if you notice any bleeding after sex. If the bleeding does not stop, contact the hospital straight away.
- Use a condom and some silicone-based or water-based lubricant if you give or receive anal sex. This helps prevent bleeding or infection.
- Never use the same condom for anal then vaginal or oral sex.
- Clean sex toys, dildos or other objects before you use them. Or cover them with a condom. If you use one for anal sex, clean it or change the condom before you use it for vaginal sex. If a partner uses it too, clean it or change the condom before you use it again.
- Using condoms and dental dams helps protect you from sexually transmitted infections (STIs). This is especially important if your cancer treatment affects how your body fights infections. Again, if you use a lubricant, only use a silicone-based or water-based product with condoms or dental dams.
Lubricants
Lubricants are gels or liquids you can use before or during sex. Using lubricant can make penetration or sexual touching feel good. It can also make it feel easier and more comfortable.
Lubricants can be water-based, silicone-based or oil-based. Always check the instructions to confirm what type you are using. Try to use ones that do not contain anything that can cause irritation, such as:
- scents
- spermicides
- preservatives
- parabens.
There are many different brands of lubricant. Some products are available through the NHS. Your cancer team can explain which type would be best for you. Types of lubricants include YES, SILK and Sutil luxe.
Some people find that using a water-based lubricant and an oil-based lubricant together is helpful – for example, YES double glide. Others find that silicone-based lubricants can last a bit longer than water-based.
You should only use a silicone-based or water-based lubricant with a condom, dental dam, latex cap (diaphragm) and latex sex toys. Oil-based lubricants can make condoms, dental dams and latex caps tear. This stops them from working.
You can also buy lubricants from a pharmacy, other shops including your local supermarket or online.
Who can help if cancer affects your sex life
If your sexual well-being is affected before, during or after cancer treatment, this does not mean your sex life is over. There may be advice, support or treatments that can help. Your healthcare team is a good place to start if you are worried. Try not to let embarrassment stop you from asking for help. Your healthcare team are used to talking about sex.
Talk to your:
- GP or practice nurse
- cancer doctor
- specialist nurse
- local sexual health service
- therapeutic radiographer, if you are having radiotherapy.
They may offer advice or treatments that can help. Or they may refer you to someone else if you need more help. This might be:
- another healthcare professional in your cancer team
- a clinic that manages changes, such as erectile dysfunction or early menopause
- a physiotherapist – a professional who may give you information and exercises that can improve some problems
- a gynaecologist – a doctor who treats female reproductive system problems
- a urologist – a doctor who treats bladder or male reproductive system problems
- an endocrinologist – a doctor who treats hormonal problems such as low testosterone.
Talking about sex with your healthcare team
Sometimes it helps to talk about sexual problems. Your healthcare team may arrange for you to talk to a counsellor, psychologist, psychiatrist or sex therapist. These professionals all work in different ways. But they can all help you understand and cope with your feelings or any changes.
It can be difficult to start a conversation about sex with someone from your healthcare team. Some people feel embarrassed or uncomfortable talking about something so personal. But it is important to get the right information when you need it. You can ask your healthcare team about anything before, during or after cancer treatment. You do not have to be in a relationship or having sex to have questions or need support.
A healthcare professional may not ask about your sexual well-being unless they know you want to talk about it. Tell them if you have questions or are worried about anything.
What is sex therapy?
Sex therapists are experts in sexual well-being. They can help with physical, emotional and relationship issues that affect sexual function or well-being. Some sex therapists are also doctors, nurses or other healthcare professionals, such as radiographers.
You can talk to a sex therapist about:
- your sex life before cancer
- your sex life during and after cancer treatment
- any physical sexual difficulties you have
- your thoughts and feelings
- your relationships.
Sex therapy can help you think about any physical changes and how to adjust to those changes. It can also help you explore different ways of enjoying sex. The therapist may suggest exercises to help you with any problems.
Therapists can also help partners. If you have a partner and feel comfortable including them in therapy, this can help you both.
The College of Sexual and Relationship Therapists and the Institute of Psychosexual Medicine have a list of professional therapists on their websites. Relate, Relate NI and Relationships Scotland may also be able to offer relationship counselling for a fee.
Tips for talking
- You may find it useful to prepare before you talk to a healthcare professional. You may find some of the following tips helpful:
- Think about who you want to talk to. Is there someone in your healthcare team you feel more comfortable with?
- Think about what information you want. For example, you may want to know why you have lost interest in sex since starting treatment, whether it will improve and what might help.
- Write down the questions you want to ask.
- Practise what you want to say.
- At the start of your appointment, tell the healthcare professional you would like some time to ask questions.
- Do not worry about using the right medical words about sex or your body. Use the words you understand and feel comfortable using.
- If something is not clear, ask the healthcare professional to explain again.
If you identify as LGBT+
Your healthcare team are there to support you and treat you in a way you feel comfortable with. There may be times when it helps them to know your gender identity or sexual orientation. It may help you feel supported. And your healthcare team can give the right information and support to you and your partner, if you have one.
The side effects of cancer treatments are often the same whatever your sexual orientation or gender identity. But as an LGBTQ+ person, you may have some specific questions about how these may affect your sexual well-being. And some side effects may be more of a problem depending on your body and the type of sex you have.
If your healthcare team cannot help, they can refer you to a sex therapist or another specialist who can. Or you may be able to get advice and support from:
- your local sexual health service
- a transgender sexual health service
- the LGBT Foundation
- our online community.
Many people have good relationships with their healthcare team. But sometimes it can be more complicated. Support is available if you feel you have been treated unfairly or are unhappy with your treatment. The Equality Advisory and Support Service (EASS) can give advice and support if you are in England, Scotland or Wales. If you are in Northern Ireland, contact the Equality Commission for Northern Ireland.
We have more information about navigating healthcare, cancer and cancer treatment for LGBTQ+ people. We also have information specifically about trans and non-binary people and cancer.
Coping with your feelings about cancer and sex
Your thoughts and feelings have a powerful effect on your sexual well-being. Being diagnosed with cancer can cause strong emotions.
How you feel about yourself sexually may also change if you:
- are feeling less in control
- feel weak or tired
- feel your role has changed at home or work
- have changes to how your body looks or works.
Whatever feelings you have, it can help to talk to someone. You may not need advice. It is often helpful to have someone just listen.
Try to find someone that you trust and feel comfortable talking to. This could be a partner, a family member, a friend or a professional (GP, cancer doctor or specialist nurse).
Talking to someone who has been through a similar treatment or situation can also help. Sometimes your cancer doctor or specialist nurse can arrange for you to talk to someone like this. Or you could join a cancer support group, or our Online Community.
Some support groups are for anyone affected by cancer or a type of cancer. Some are for anyone of a specific gender or sexual orientation. Some groups meet face to face and others meet online.
You may prefer to get support from a helpline or through email or webchat. These can be anonymous, and it might feel easier to talk about sex and ask questions this way.
We have more information about coping with your feelings and about cancer and relationships.